Chapter: Array | Let us C solution with details description and tutorials | yashwant kanetkar
[D] Answer the following: | | | |
(a) Twenty-five numbers are entered from the keyboard into an array. The number to be searched is entered through the keyboard by the user. Write a program to find if the number to be searched is present in the array and if it is present, display the number of times it appears in the array.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/*
[D] Answer the following:
(a) Twenty-five numbers are entered from the keyboard into an array. The number to be searched is entered through the keyboard by the user. Write a program to find if the number to be searched is present in the array and if it is present, display the number of times it appears in the array.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[25];
int a,d,i;
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
{
printf("\nKey %d) value",i);
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
printf("\n25 numbers stored, enter any integer again");
scanf("%d",&d);
for(i=0,a=0;i<25;i++)
{
if(arr[i]==d)
a++;
}
if(a>0)
printf("\nThe integer appeared %d times in the array",a);
else
printf("\nThe integer did not appear in the array");
getch();
return 0;
}
(b) Twenty-five numbers are entered from the keyboard into an array. Write a program to find out how many of them are positive, how many are negative, how many are even and how many odd.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/*
(b) Twenty-five numbers are entered from the keyboard into an array.
Write a program to find out how many of them are positive, how many
are negative, how many are even and how many odd.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int a[25],odd=0,even=0,neg=0,pos=0,i;
printf("\n Please enter 25 elements : ");
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
{
if(a[i]>=0)
pos++;
else
neg++;
if(a[i]%2==0)
even++;
else
odd++;
}
printf("\n Positive : %d",pos);
printf("\n Negative : %d",neg);
printf("\n Even : %d",even);
printf("\n Odd : %d",odd);
getch();
return 0;
}
(c) Implement the Selection Sort, Bubble Sort and Insertion sort algorithms on a set of 25 numbers. (Refer Figure 8.11 for the logic of the algorithms) ? Selection sort
? Bubble Sort
? Insertion Sort
figure see in book
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/*d (c) Implement the Selection Sort, Bubble Sort and Insertion sort algorithms on
a set of 25 numbers. (Refer Figure 8.11 for the logic of the algorithms)
? Selection sort
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[25];
int a,b,d,i;
printf("\n Input 25 numbers into array: ");
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
{
printf("\n Key the %d value: ",i);
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
printf("\n Starting selection sorting");
for(i=0;i<24;i++)
{
for(d=i+1;d<25;d++)
{
a=arr[i];
b=arr[d];
arr[i]=b;
arr[d]=a;
}
}
printf("\nSelection sorting done");
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
printf("\n%d) value is %d",i,arr[i]);
getch();
return 0;
}
(d) Implement the following procedure to generate prime numbers from 1 to 100 into a program. This procedure is called sieve of Eratosthenes.
step 1
Fill an array num[100] with numbers from 1 to 100
step 2
Starting with the second entry in the array, set all its multiples to zero.
step 3
Proceed to the next non-zero element and set all its multiples to zero.
step 4
Repeat step 3 till you have set up the multiples of all the non-zero elements to zero
step 5
At the conclusion of step 4, all the non-zero entries left in the array would be prime numbers, so print out these numbers.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/*
(d) Implement the following procedure to generate prime numbers from 1 to 100 into a program. This procedure is called sieve of Eratosthenes.
step 1
Fill an array num[100] with numbers from 1 to 100
step 2
Starting with the second entry in the array, set all its multiples to zero.
step 3
Proceed to the next non-zero element and set all its multiples to zero.
step 4
Repeat step 3 till you have set up the multiples of all the non-zero elements to zero
step 5
At the conclusion of step 4, all the non-zero entries left in the array would be prime numbers, so print out these numbers.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main()
{
int num[100];
int i,a;
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
num[i]=i+1;
}
for(i=2;i<100;i++)
{
for(a=2;a<num[i];a++)
{
if(num[i]%a==0)
num[i]=0;
}
}
num[0]=0;
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
if(num[i]!=0)
printf(" %d ",num[i]);
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
[I] Attempt the following:
(a) Write a program to copy the contents of one array into another in the reverse order.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/* i (a) Write a program to copy the contents of one array into another in the reverse order.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int arr1[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int arr2[5];
int i,k;
for (i=4,k=0;i>=0;i--,k++)
arr2[k]=arr1[i];
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
printf("\nValue of arr2[%d] is %d",i,arr2[i]);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(b) If an array arr contains n elements, then write a program to check if arr[0] = arr[n-1], arr[1] = arr[n-2] and so on.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* i b) If an array arr contains n elements, then write a program to check
if arr[0] = arr[n-1], arr[1] = arr[n-2] and so on.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int arr[25];
int i,*j,k;
j=arr;
printf("\n Input 25 integers:");
for(i=0;i<25;i++,j++)
{
printf("\n Key in the %d) value",i+1);
scanf("%d",&*j);
}
for(i=0;i<25;i++)
{
for(k=24;k>i;k--)
if(arr[i]==arr[k])
printf("\n Array [%d] = Array[%d]",i,k);
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(c) Find the smallest number in an array using pointers.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* i (c) Find the smallest number in an array using pointers.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
void change();
int main() //main function
{
int a[10];
int i,j;
printf("n Enter the 10 Array elements: ");
for(i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
change(a);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
void change(int*b)
{
int i,j,temp;
for(i=1;i<=9;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<=9;j++)
{
if(b[i]) {
temp=b[i];
b[i]=b[j];
b[j]=temp;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<=9;i++)
{
}
printf("The smallest number is=%d",b[9]);
}
(d) Write a program which performs the following tasks:
? initialize an integer array of 10 elements in main( )
? pass the entire array to a function modify( )
? in modify( ) multiply each element of array by 3
? return the control to main( ) and print the new array elements in main( )
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* i (d) Write a program which performs the following tasks:
? initialize an integer array of 10 elements in main( )
? pass the entire array to a function modify( )
? in modify( ) multiply each element of array by 3
? return the control to main( ) and print the new array elements in main( )
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int arr[10]; int i,*j; j=arr;
printf("\nlnput 10 integers into the array");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("\nKey in the %d) value",i+1);
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
modify(j,i);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("\nThe value in arr[%d] is %d",i,arr[i]);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
modify(int *j,int i)
{
int m;
for(m=0;m<i;m++,j++)
*j*=3;
}
(e) The screen is divided into 25 rows and 80 columns. The characters that are displayed on the screen are stored in a special memory called VDU memory (not to be confused with ordinary memory). Each character displayed on the screen occupies two bytes in VDU memory. The first of these bytes contains the ASCII value of the character being displayed, whereas, the second byte contains the colour in which the character is displayed. For example, the ASCII value of the character present on zeroth row and zeroth column on the screen is stored at location number 0xB8000000. Therefore the colour of this character would be present at location number 0xB8000000 + 1. Similarly ASCII value of character in row 0, col 1 will be at location 0xB8000000 + 2, and its colour at 0xB8000000 + 3. With this knowledge write a program which when executed would keep converting every capital letter on the screen to small case letter and every small case letter to capital letter. The procedure should stop the moment the user hits a key from the keyboard. This is an activity of a rampant Virus called Dancing Dolls. (For monochrome adapter, use 0xB0000000 instead of 0xB8000000).
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* i (e) The screen is divided into 25 rows and 80 columns. The characters that
are displayed on the screen are stored in a special memory called VDU
memory (not to be confused with ordinary memory). Each character displayed on
the screen occupies two bytes in VDU memory. The first of these bytes contains
the ASCII value of the character being displayed, whereas, the second byte contains
the colour in which the character is displayed. For example, the ASCII value of the
character present on zeroth row and zeroth column on the screen is stored at
location number 0xB8000000. Therefore the colour of this character would be
present at location number 0xB8000000 + 1. Similarly ASCII value of character
in row 0, col 1 will be at location 0xB8000000 + 2, and its colour at 0xB8000000 + 3.
With this knowledge write a program which when executed would keep converting every
capital letter on the screen to small case letter and every small case letter to
capital letter. The procedure should stop the moment the user hits a key from the
keyboard. This is an activity of a rampant Virus called Dancing Dolls.
(For monochrome adapter, use 0xB0000000 instead of 0xB8000000).
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
More than one dimension [L] Attempt the following:
(a) How will you initialize a three-dimensional array threed[3][2][3]? How will you refer the first and last element in this array?
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L a) How will you initialize a three-dimensional array threed[3][2][3]? How will
you refer the first and last element in this array?
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int i,j,k;
for (i =0;i<3;i++ )
{
for (j=0;j<2;j++)
{
for (k=0;k<3;k++)
{
//Initialize element array[i][j][z] = some value;
}
}
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(b) Write a program to pick up the largest number from any 5 row by 5 column matrix.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* l (b) Write a program to pick up the largest number from any 5 row by 5 column matrix.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int a[5][5]={ {21,12,71,9,7},{13,54,56,2,5},
{13,43,89,22,33},
{14,15,17,13,44},
{45,3,1,23,13}
};
int i,j,big;
big=a[0][0];
printf("\nThe 5*5 matrix in:\n");
for(i=0;i<=4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=4;j++)
{
printf("%d\t",a[i][j]);
if(a[i][j]>big)
big=a[i][j];
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\nlargest no. in matrix is%d",big);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(c) Write a program to obtain transpose of a 4 x 4 matrix. The transpose of a matrix is obtained by exchanging the elements of each row with the elements of the corresponding column.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/* l (c) Write a program to obtain transpose of a 4 x 4 matrix. The transpose
of a matrix is obtained by exchanging the elements of each row with the
elements of the corresponding column.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int arr[4][4];
int i,j,a,b,f;
printf("\nInput numbers to 4*4 matrix");
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
printf("\nKey in the [%d][%d]) value",i+1,j+1);
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0,f=0;j<4;j++)
{
if(i!=j&&f==0)
continue;
a=arr[i][j];
b=arr[j][i];
arr[i][j]=b;
arr[j][i]=a;
f=1;
}
}
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
printf("%d ",arr[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(d) Very often in fairs we come across a puzzle that contains 15 numbered square pieces mounted on a frame. These pieces can be moved horizontally or vertically. A possible arrangement of these pieces is shown below:
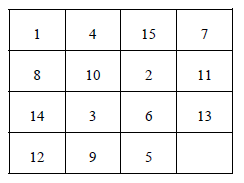
Figure 8.12 As you can see there is a blank at bottom right corner. Implement the following procedure through a program: Draw the boxes as shown above. Display the numbers in the above order. Allow the user to hit any of the arrow keys (up, down, left, or right). If user hits say, right arrow key then the piece with a number 5 should move to the right and blank should replace the original position of 5. Similarly, if down arrow key is hit, then 13 should move down and blank should replace the original position of 13. If left arrow key or up arrow key is hit then no action should be taken. The user would continue hitting the arrow keys till the numbers aren't arranged in ascending order. Keep track of the number of moves in which the user manages to arrange the numbers in ascending order. The user who manages it in minimum number of moves is the one who wins. How do we tackle the arrow keys? We cannot receive them using scanf( ) function. Arrow keys are special keys which are identified by their 'scan codes'. Use the following function in your program. It would return the scan code of the arrow key being hit. Don't worry about how this function is written. We are going to deal with it later. The scan codes for the arrow keys are: up arrow key - 72 down arrow key - 80 left arrow key - 75 right arrow key - 77
/* Returns scan code of the key that has been hit */
#include "dos.h" getkey( )
{
union REGS i, o ;
while ( !kbhit( ) )
i.h.ah = 0 ; int86 ( 22, &i, &o ) ;
return ( o.h.ah ) ;
}
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L d) Very often in fairs we come across a puzzle that contains 15 numbered square
pieces mounted on a frame. These pieces can be moved horizontally or vertically.
A possible arrangement of these pieces is shown below:
Figure 8.12 As you can see there is a blank at bottom right corner.
Implement the following procedure through a program: Draw the boxes as
shown above. Display the numbers in the above order. Allow the user to
hit any of the arrow keys (up, down, left, or right). If user hits say,
right arrow key then the piece with a number 5 should move to the right
and blank should replace the original position of 5. Similarly, if down
arrow key is hit, then 13 should move down and blank should replace the
original position of 13. If left arrow key or up arrow key is hit then no
action should be taken. The user would continue hitting the arrow keys till the
numbers aren't arranged in ascending order. Keep track of the number of moves in
which the user manages to arrange the numbers in ascending order. The user who
manages it in minimum number of moves is the one who wins. How do we tackle the
arrow keys? We cannot receive them using scanf( ) function. Arrow keys are special
keys which are identified by their 'scan codes'. Use the following function in
your program. It would return the scan code of the arrow key being hit. Don't
worry about how this function is written. We are going to deal with it later.
The scan codes for the arrow keys are: up arrow key - 72 down arrow key -
80 left arrow key - 75 right arrow key - 77
Returns scan code of the key that has been hit
#include "dos.h" getkey( )
{
union REGS i, o ;
while ( !kbhit( ) )
i.h.ah = 0 ; int86 ( 22, &i, &o ) ;
return ( o.h.ah ) ;
}
*/
#include "dos.h" getkey( )
{
union REGS i, o ;
while ( !kbhit( ) )
i.h.ah = 0 ; int86 ( 22, &i, &o ) ;
return ( o.h.ah ) ;
}
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
void creategrid();
int g,c;
int arr[16]={1,4,15,7,8,10,2,11,14,3,6,13,12,9,5,0};
clrscr();
creategrid();
printarray(arr);
for(g=15,c=0;;)
{
int k,a,b,i;
k=getkey();
if(k==80)
{
if((g-4)<0) a="arr[g-4];" b="arr[g];" k="="72)">15)
continue;
a=arr[g+4];
b=arr[g];
arr[g+4]=b;
arr[g]=a;
go(g);
printf("%d",arr[g]);
go(g+4);
printf("%c%c",0,0);
go(g+4);
c++;
g+=4;
}
if(k==75)
{
if(g==3g==7g==11g==15)
continue;
a=arr[g+1];
b=arr[g];
arr[g+1]=b;
arr[g]=a;
go(g);
printf("%d",arr[g]);
go(g+1);
printf("%c%c",0,0);
go(g+1);
c++;
g+=1;
}
if(k==77)
{
if(g==0g==4g==8g==12)
continue;
a=arr[g-1];
b=arr[g];
arr[g-1]=b;
arr[g]=a;
go(g);
printf("%d",arr[g]);
go(g-1);
printf("%c%c",0,0);
go(g-1);
c++;
g-=1;
}
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
{
if(arr[i]!=i+1)
break;
if(arr[i]==(i+1)&&i==14)
{
gotoxy(6,24);
printf("\nNumber of moves to complete is %d",c);
exit();
}
}
}
}
go(int g)
{
switch(g)
{
case 0:
gotoxy(8,5);
break;
case 1:
gotoxy(12,5);
break;
case 2:
gotoxy(16,5);
break;
case 3:
gotoxy(20,5);
break;
case 4:
gotoxy(8,9);
break;
case 5:
gotoxy(12,9);
break;
case 6:
gotoxy(16,9);
break;
case 7:
gotoxy(20,9);
break;
case 8:
gotoxy(8,13);
break;
case 9:
gotoxy(12,13);
break;
case 10:
gotoxy(16,13);
break;
case 11:
gotoxy(20,13);
break;
case 12:
gotoxy(8,17);
break;
case 13:
gotoxy(12,17);
break;
case 14:
gotoxy(16,17);
break;
case 15:
gotoxy(20,17);
break;
}
}
getkey()
{
union REGS i,o;
while(!kbhit())
;
i.h.ah=0;
int86(22,&i,&o);
return(o.h.ah);
}
printarray(int *m)
{
int a,b,i,j;
for(a=5,i=0;a<=17;a+=4,i++)
{
for(b=8,j=0;b<=20;b+=4,j++)
{
gotoxy(b,a);
printf("%d",*(m+(i*4)+j));
}
}
gotoxy(20,17);
printf("%c",0);
}
void creategrid()
{
int a,b;
for(a=3;a<=19;a+=4)
{
for(b=6;b<=22;b++)
{
if(b==6(b-6)%4==0)
{
if(a==3)
{
if(b==6)
{
gotoxy(6,3);
printf("%c",218);
}
else if(b==22)
{
gotoxy(22,3);
printf("%c",191);
}
else
{
gotoxy(b,3);
printf("%c",194);
}
}
else if(a==19)
{
if(b==6)
{
gotoxy(6,19);
printf("%c",192);
}
else if(b==22)
{
gotoxy(22,19);
printf("%c",217);
}
else
{
gotoxy(b,19);
printf("%c",193);
}
}
else
{
if(b==6)
{
gotoxy(6,a);
printf("%c",195);
}
else if(b==22)
{
gotoxy(22,a);
printf("%c",180);
}
else
{
gotoxy(b,a);
printf("%c",197);
}
}
}
else
{
printf("%c",196);
}
}
}
for(b=6;b<=22;b+=4)
{
for(a=4;a<=18;a++)
{
if((a-3)%4==0)
continue;
else
{
gotoxy(b,a);
printf("%c",179);
}
}
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(e) Those readers who are from an Engineering/Science background may try writing programs for following problems.
(1) Write a program to add two 6 x 6 matrices.
(2) Write a program to multiply any two 3 x 3 matrices.
(3) Write a program to sort all the elements of a 4 x 4 matrix.
(4) Write a program to obtain the determinant value of a 5 x 5 matrix.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* l (e) Those readers who are from an Engineering/Science background may try writing programs for following problems.
(1) Write a program to add two 6 x 6 matrices.
(2) Write a program to multiply any two 3 x 3 matrices.
(3) Write a program to sort all the elements of a 4 x 4 matrix.
(4) Write a program to obtain the determinant value of a 5 x 5 matrix.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function //program to add two 6*6 matrix
{
int a[6][6],b[6][6],c[6][6],i,j;
printf("Enter the First matrix->");
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("\nEnter the Second matrix->");
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
printf("\nThe First matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
printf("%d\t",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\nThe Second matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
printf("%d\t",b[i][j]);
}
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
printf("\nThe Addition of two matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
printf("%d\t",c[i][j]);
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
// function to multiply 3*3 matrix
void multiply_3by3()
{
int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3],i,j,k;
printf("Enter elements of A: ");
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
for(j=0;j<=2;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("Enter elements of B: ");
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
for(j=0;j<=2;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
printf("A:");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
printf(" ");
}
printf("B ");
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=2;j++)
printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
printf(" ");
}
k=0;
while(k<=2)
{
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
{
int sum=0;
for(j=0;j<=2;j++)
sum=sum+a[i][j]*b[j][k];
c[i][k]=sum;
}
k++;
}
printf("Result is as: ");
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=2;j++)
printf("%d ",c[i][j]);
printf(" ");
}
getch();
}
int sortnbynmatrix(){ // define 4 size as 4 by 4 instead of entering no of rows and cols
int rows,cols,jndex,input;
int sum2=0;
printf("Enter rows and cols number for sorting: ");
scanf("%d %d",&rows,&cols);
int matrix[rows][cols]; // as per size allocate space
int sum[rows][cols];
int temp[rows][cols];
int transpose [cols][rows];
int index,kndex,tndex,gndex,lndex;
int rows_sum[rows];
printf("Enter power:");
scanf("%d",&input);
for (index = 0; index < rows; index++)
{
rows_sum[index]=0;
for (kndex = 0; kndex < cols; kndex++)
{
matrix[index][kndex] = 0;
sum[index][kndex] = 0;
temp[index][kndex] = 0;
transpose[index][kndex] = 0;
}//
}//
printf("Enter value in a row for a matrix: "); // input elements
for (index = rows - 1;index >= 0; index--)
{
for (kndex = cols - 1; kndex >= 0; kndex--)
{
scanf("%d", &matrix[index][kndex]);
transpose[kndex][index] = matrix[index][kndex];
}
}
getchar();
for (index = 0; index < rows; index++)
{
for (kndex = 0; kndex < cols; kndex++)
rows_sum[index]=rows_sum[index]+matrix[index][kndex];
printf("\n");
}
// for displaying results
for (index = 0; index < rows; index++)
{
for (kndex = 0; kndex < cols; kndex++)
printf(" %d ", sum[index][kndex]);
printf("\n"); // new line
}
return 0;
}// function ends
from L.(f-i) match the following. Solution not available
(j) Write a program that interchanges the odd and even components of an array.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (j) Write a program that interchanges the odd and even components of an array.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int arr[10] = {6,3,4,3,1,6,15,2,32,9};
int size = 10;
int End_Count = size-1;
int Start_Count = 0;
int sort_array[10];
int temp,i;
for(temp = 0; temp<size; temp++) // for interchanging odd and even element
{
if(arr[temp]%2)
{
sort_array[End_Count] = arr[temp];
End_Count--;
}
else
{
sort_array[Start_Count] = arr[temp];
Start_Count++;
}
}
for(i=0;i<10;i++) // for displaying element
{
printf(" %d ",sort_array[i]);
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(k) Write a program to find if a square matrix is symmetric.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (k) Write a program to find if a square matrix is symmetric.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int i,j,a[10][10],b[10][10],temp,n;
printf("\n Enter the dimensions of matrix:: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\n Enter the elemnts of matrix::\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); // take inputs
printf("\n Original Matrix was: ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
printf("\t%d",a[i][j]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
b[j][i]=a[i][j];
}
printf("\nTranspose Matrix is:: ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
printf(" %d ",b[i][j]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=b[i][j])
{
printf("\n Matrix is not symmatric.");
exit(0);
}
}
}
printf("\n Matrix is symmatric.");
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(l) Write a function to find the norm of a matrix. The norm is defined as the square root of the sum of squares of all elements in the matrix.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (l) Write a function to find the norm of a matrix. The norm is defined
as the square root of the sum of squares of all elements in the matrix.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
#include <math.h>
int main() //main function
{
float arr[2][2];
int i,j,k=0;
float *l;
l=&k;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf(" Key in the [%d][%d] value: ",i+1,j+1);
printf(" ");
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
}
}
norm(arr,2,2,1);
printf(" \n The value of the norm of matrix is %f",*l);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
norm(int *q,int i,int j,float *c) // function
{
int sum,a,b;
int *d;
for(a=0,sum=0;a<i;a++)
{
for(b=0;b<j;b++)
{
d=q+a*2+b; sum=sum+pow(*d, 2);
}
}
*c=sqrt(sum) ; // square root function
}
(m) Given an array p[5], write a function to shift it circularly left by two positions. Thus, if p[0] = 15, p[1]= 30, p[2] = 28, p[3]= 19 and p[4] = 61 then after the shift p[0] = 28, p[1] = 19, p[2] = 61, p[3] = 15 and p[4] = 30. Call this function for a (4 x 5 ) matrix and get its rows left shifted.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (m) Given an array p[5], write a function to shift it circularly
left by two positions. Thus, if p[0] = 15, p[1]= 30, p[2] = 28,
p[3]= 19 and p[4] = 61 then after the shift p[0] = 28, p[1] = 19,
p[2] = 61, p[3] = 15 and p[4] = 30. Call this function for a
(4 x 5 ) matrix and get its rows left shifted.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int i,j,p[]={15,30,28,19,61};
int a[4][5];
printf("Array before shift:\n\n");
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {
printf("%2d ",p[i]);
}
func(p);
printf("\n\nArray after shift:\n\n");
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {
printf("%2d ",p[i]);
}
printf("\n\n\nenter the elements of 4x5 matrix: \n\n");
for(i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(j=0;j<5;j++) {
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("matrix you enterd before shift: \n\n");
for(i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(j=0;j<5;j++) {
printf("%2d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\nafter shift:\n\n");
/* shift the rows of matrix */
for(i=0;i<4;i++) {
func(a[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<4;i++) {
for(j=0;j<5;j++) {
printf("%2d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
func(int q[5]) {
int a,t1,t2,t3;
t1=q[0];
t2=q[1];
q[0]=q[2];
q[1]=q[3];
q[2]=q[4];
q[3]=t1;
q[4]=t2;
return q[5];
}
/*
refer source: http://letuscalllessons.blogspot.com/2014/01/chapter-8-arrays.html
*/
(n) A 6 x 6 matrix is entered through the keyboard and stored in a 2-dimensional array mat[7][7]. Write a program to obtain the Determinant values of this matrix.
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
Chapter: Array
/* L (n) A 6 x 6 matrix is entered through the keyboard and stored in a
2-dimensional array mat[7][7]. Write a program to obtain the
Determinant values of this matrix.
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
// Refer to : http://easy-learn-c-language.blogspot.in/2013/02/numerical-methods-determinant-of-nxn.html
// Note: just initialize n=6
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
(o) For the following set of sample data, compute the standard deviation and the mean. -6, -12, 8, 13, 11, 6, 7, 2, -6, -9, -10, 11, 10, 9, 2 The formula for standard deviation is
where xi is the data item and x is the mean
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/*L (o) For the following set of sample data, compute the standard
deviation and the mean. -6, -12, 8, 13, 11, 6, 7, 2, -6, -9,
-10, 11, 10, 9, 2 The formula for standard deviation is
where xi is the data item and x is the mean.

*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
// Problem is not hard. It is only mathematics and only solution dificulties is to transform math into
// programatically.
int a[15]={-6,-12,8,13,11,6,7,2,-6,-9,-10,11,10,9,2}; // array storage
int i,j;
float temp,sd,sum=0,mean,x;
printf("\ndata set: \n\n");
for(i=0;i<15;i++) {
printf(" %3d ",a[i]); // display value
}
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i<15;i++) {
sum=sum+a[i]; /* adding all the numbers for calculating mean*/
}
mean=sum/15; /* calculating the mean mean = sum/total_no. use of math formula */
for(i=0;i<15;i++) {
a[i]=pow((a[i]-mean),2); // calculation of (xi-mean ) ^ 2
x=x+a[i];
}
temp=x/15; // use of formula calculation of ( (xi-mean ) ^ 2 ) /n here n=15
sd=sqrt(temp); // function for square root
printf("\n mean= %f standard deviation = %f",mean,sd); // display data
getch(); // hold screen
return 0; // return int value
}
// Solution refered: http://letuscalllessons.blogspot.com/
(p) The area of a triangle can be computed by the sine law when 2 sides of the triangle and the angle between them are known. Area = (1 / 2 ) ab sin ( angle ) Given the following 6 triangular pieces of land, write a program to find their area and determine which is largest,
Plot No. a b angle
1 137.4 80.9 0.78
2 155.2 92.62 0.89
3 149.3 97.93 1.35
4 160.0 100.25 9.00
5 155.6 68.95 1.25
6 149.7 120.0 1.75
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (p) The area of a triangle can be computed by the sine law when 2 sides of the triangle and the angle between them are known. Area = (1 / 2 ) ab sin ( angle ) Given the following 6 triangular pieces of land, write a program to find their area and determine which is largest,
Plot No. a b angle
1 137.4 80.9 0.78
2 155.2 92.62 0.89
3 149.3 97.93 1.35
4 160.0 100.25 9.00
5 155.6 68.95 1.25
6 149.7 120.0 1.75
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
float a[6][3]={ {137.4, 80.9, 0.78},
{155.2, 92.62, 0.89},
{149.3, 97.93, 1.35},
{160.0, 100.25, 9.00},
{155.6, 68.95, 1.25},
{149.7, 120.0, 1.75} };
float big=0,area;
int sr=0,i;
for(i=0;i<6;i++) { // loop to detect area for all plot
area=(1.0/2.0)*a[i][0]*a[i][1]*sin(a[i][2]); // math formula given above for all
if(area>big) { // big =0 initially . So, big = area[0] then compare and detect big
big=area;
sr=i;
}
}
printf("\n Plot no. %d is the biggest.\n",sr);
printf("\nArea of plot no. %d = %f\n",sr,big);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
// Solution refered: http://letuscalllessons.blogspot.com
(q) For the following set of n data points (x, y), compute the correlation coefficient r,
x y
34.22 102.43
39.87 100.93
41.85 97.43
43.23 97.81
40.06 98.32
53.29 98.32
53.29 100.07
54.14 97.08
49.12 91.59
40.71 94.85
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L q) For the following set of n data points (x, y), compute the correlation coefficient r,
x y
34.22 102.43
39.87 100.93
41.85 97.43
43.23 97.81
40.06 98.32
53.29 98.32
53.29 100.07
54.14 97.08
49.12 91.59
40.71 94.85
55.15 94.65

*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
float a[][2]={ {34.22,102.43}, // initiallization of value
{39.87,100.93},
{41.85,97.43},
{43.23,97.81},
{40.06,98.32},
{53.29,98.32},
{53.29,100.07},
{54.14,97.08},
{49.12,91.59},
{40.71,94.85},
{55.15,94.65} };
int i,n=0;
float x2,y2,x,y,x_y,n_x2,n_y2,r;
for(i=0;i<11;i++) {
x2= x2 + ( a[i][0] * a[i][0] ); /* computing square of x */
y2= y2 + ( a[i][1] * a[i][1] ); /* computing square of y */
x= x + a[i][0]; /* computing total of x */
y= y + a[i][1]; /* computing total of y */
x_y= x_y + ( a[i][0] * a[i][1] ); /* computing total of x * y */
n++;
}
n_x2= n * x2;
n_y2= n * y2;
r= ( x_y - x*y )/sqrt((n_x2-x2) * (n_y2-y2)); // formula math
printf(" sum of square of x = %f\n\n",x2);
printf(" sum of square of y = %f\n\n",y2);
printf(" sum of x = %f\n\n",x);
printf(" sum of y = %f\n\n",y);
printf(" sum of x * y = %f\n\n",x_y);
printf(" sum of n*x2 = %f\n\n",n_x2);
printf(" sum of n*y2 = %f\n\n",n_y2);
printf("\n\n\nCorrelation cofficient = %f\n",r);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
// Solution refered: http://letuscalllessons.blogspot.com/
(r) For the following set of point given by (x, y) fit a straight line given by y = a + bx
where,
x y
3.0 1.5
4.5 2.0
5.5 3.5
6.5 5.0
7.5 6.0
8.5 7.5
8.0 9.0
9.0 10.5
9.5 12.0
10.0 14.0
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (r) For the following set of point given by (x, y) fit a straight line given by y = a + bx
where,
x y
3.0 1.5
4.5 2.0
5.5 3.5
6.5 5.0
7.5 6.0
8.5 7.5
8.0 9.0
9.0 10.5
9.5 12.0
10.0 14.0
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
float data[][2]= { {3.0,1.5},
{4.5,2.0},
{5.5,3.5},
{6.5,5.0},
{7.5,6.0},
{8.5,7.5},
{8.0,9.0},
{9.0,10.5},
{9.5,12.0},
{10.0,14.0} };
int i,n=0;
float sx,sy,x2,y2,xy,a,b,Y;
for(i=0;i<10;i++) {
sx = sx + data[i][0];
sy = sy + data[i][1];
x2= x2 + ( data[i][0] * data[i][0] );
y2= y2 + ( data[i][1] * data[i][1] );
xy = xy + ( data[i][0] * data[i][1] );
n++;
}
printf(" sum of x = %f\n",sx);
printf(" sum of y = %f\n",sy);
printf(" sum of x2 = %f\n",x2);
printf(" sum of y2 = %f\n",y2);
printf(" sum of x*y = %f\n",xy);
printf(" total number = %d\n",n);
b = ( (n*xy) - (sx*sy) ) / ( n*x2 - (sx*sx) );
a = (sy/n) - b*(sx/n);
Y= a + b*sx ;
printf("\n\nvalue of a = %f\n\n",a);
printf("value of b = %f\n\n",b);
printf(" Y = %f \n\n",Y);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}
// solution refered: http://letuscalllessons.blogspot.com/
(s) The X and Y coordinates of 10 different points are entered through the keyboard. Write a program to find the distance of last point from the first point (sum of distance between consecutive points).
Show Solutions
Hide Solutions
/* L (s) The X and Y coordinates of 10 different points are entered through
the keyboard. Write a program to find the distance of last point from
the first point (sum of distance between consecutive points).
*/
#include <stdio.h> //header file
#include <conio.h> //header file
int main() //main function
{
int i,sqr;
double x[10],y[10],x1,y1 ,dist, sum=0.0;
printf("\nEnter the coordinates (X,Y)");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
scanf("%lf %lf",&x[i],&y[i]);
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
x1=pow((x[i+1]-x[i]),2.0); // x1= (x2-x1) * power 2 formula of math
y1=pow((y[i+1]-y[i]),2.0);
dist=sqrt(x1+y1); math formula
sum+=dist;
}
printf("\nDistance between point is= %f",sum);
getch();
return 0; // return int value
}






Comments
Post a Comment